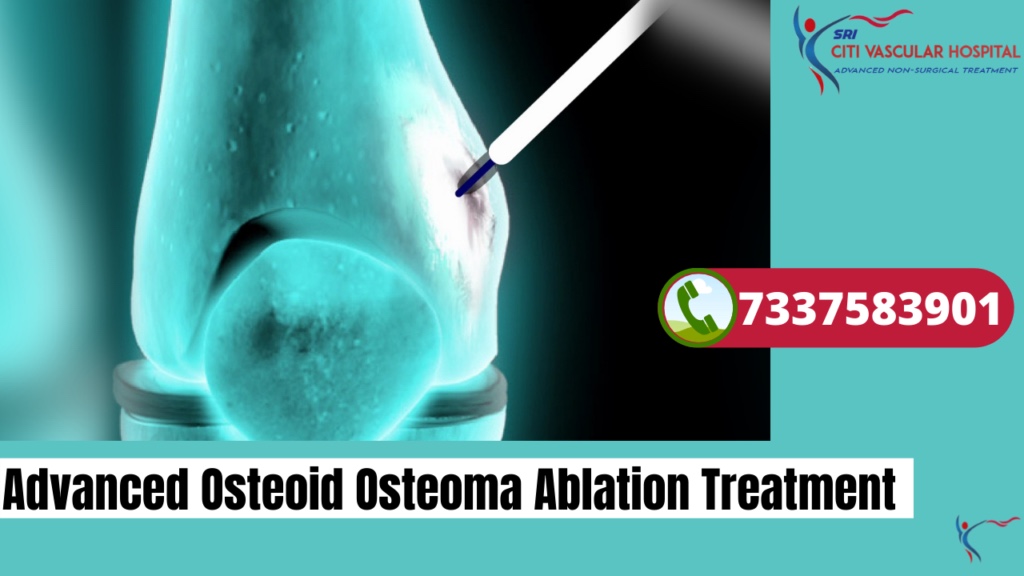
Osteoid osteoma is a benign bone tumour usually affecting children and young adults. It causes localized pain that often increases at night. The tumour can rarely resolve itself, but treatment is usually necessary to relieve pain and prevent complications.
Treatment Options for Osteoid Osteoma
Medical (Conservative) Treatment
Pan Relief Medicines (NSAIDs) :
These are often the first line of treatment to relieve pain and inflammation. Long-term NSAID use may be required, but it carries risks like gastrointestinal bleeding and kidney issues.
Minimally Invasive Treatments
Microwave Thermal Ablation (MWA): One of the gold standard for treating osteoid osteoma. A thin probe is inserted into the bone lesion under CT guidance, and heat generated by microwave energy to destroy tumour nidus. It gives high success and short hospital stays.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Similar to MWA but uses radio waves to ablate the tumor. It has similar success rate.
Cryoablation: Uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy the tumor, useful for osteoid osteomas near nerves or atypical locations.
Interstitial Laser Ablation (ILA): A laser-based treatment that is simpler than RFA and cost-effective.
MR-guided Focused Ultrasound (MRg-FUS): An emerging still in early phase, noninvasive technique using focused ultrasound waves.
Surgical Treatment
Open Surgery: Traditional surgery involves removing the tumor by cutting open the affected bone. Although effective, it usually requires a longer recovery time and may weaken the bone, leading to a risk of fracture. Surgery is now used only when minimally invasive treatments are not suitable or have failed.
Doctor confirms diagnosis of osteoid osteoma.
If pain is mild and manageable with medicines, treatment continues with observation.
If pain persists or interferes with daily life, a minimally invasive ablation procedure is recommended.
If the tumor is in a tricky location or ablation doesn’t fully remove it, surgery may be necessary.
Comparison Table of Treatment Options
|
Treatment Type |
Success Rate |
Recovery Time |
Risks/Limitations |
Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NSAIDs |
Moderate |
None, long-term use |
Side effects with prolonged use |
Mild pain, non-surgical cases |
|
Radiofrequency Ablation |
~90-97% |
Short hospital stay |
Skin burns, requires imaging guidance |
Most osteoid osteomas |
|
Cryoablation |
High |
Short hospital stay |
Less studied, nerve proximity cases |
Tumors near nerves |
|
Microwave Ablation |
Very High |
Short hospital stay |
Emerging technique |
Most typical lesion sites |
|
Interstitial Laser Ablation |
High |
Short hospital stay |
May be less available |
Alternative to RFA |
|
Surgery (Excise/Curettage) |
88-97% |
Longer, rehab needed |
Fracture risk, longer recovery |
Rare, atypical or failed ablation cases |
Always discuss with your intervention radiologist or ortho specialist about the least invasive treatment suitable for your tumour location.
If medicines control your pain, aggressive treatment may not be needed.
For quicker recovery, minimally invasive procedures like microwave thermal ablation or RFA are preferred.
Follow post-procedure care instructions carefully to avoid complications.
Get periodic imaging follow-ups to ensure the tumour is fully treated.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can osteoid osteoma resolve without treatment?
A: Yes, some osteoid osteomas shrink and disappear on their own but this may take several years and pain might persist during that time.
Q: What is the best or safest treatment option for osteoid osteoma near nerves?
A: Cryoablation or sometimes open surgery, because they give doctors more control around sensitive areas.
Q: How long is recovery after microwave or radiofrequency thermal ablation?
A: Recovery is usually quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days.
Q: Are there risks with long-term NSAID use?
A: Yes, long-term NSAID use can cause gastrointestinal bleeding, kidney damage, and other side effects.
Q: Is surgery still common for osteoid osteoma?
A: Surgery is less common now due to effective minimally invasive options like MWA or RFA but may be necessary for complicated cases.
Expert Diagnosis: Dr. Shailesh Kumar Garge's expertise in imaging and interventional procedures
Advanced Technology: State-of-the-art imaging and biopsy equipment
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Reduced scarring and faster recovery
Comprehensive Care: From diagnosis through treatment and follow-up
Patient-Cantered Approach: Compassionate care with clear communication
Don't let uncertainty about a osteoid osteoma cause unnecessary anxiety. Early evaluation provides peace of mind and ensures appropriate treatment when needed.
Contact Citi Vascular Hospital: Road No1, KPHB Colony, Hyderabad .Dr. Shailesh Kumar Garge
Call Whatsapp 7032508468
Visit us on https://citivascularcentre.com/advanced-osteoid-osteoma-ablation-treatment